
What is Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA)?
Techno-economic analysis (TEA) is a comprehensive methodology used to assess the economic viability and sustainability of emerging technologies. It integrates technical and economic aspects, providing a quantitative framework to evaluate the feasibility of implementing a technology in terms of both engineering and economic considerations. The importance of TEA lies in its ability to inform decision-makers, investors, and policymakers about the economic implications of adopting a particular technology.
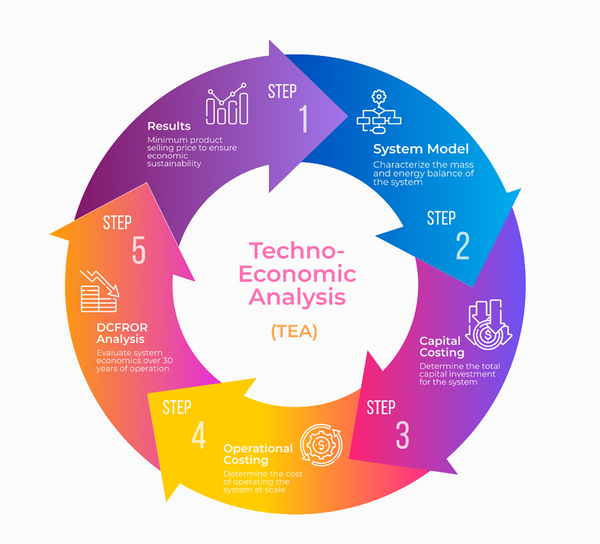
Key Steps of a Techno-Economic Analysis
Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) can be broken down into an iterative 5-step process. First, the performance of the technology is captured through dynamic system models that track mass and energy throughout the system. Next, large-scale flow rates within the facility and the desired facility output are utilized to quantify the total capital investment and annual operational costs for the fully scaled system. Afterward, economic parameters are integrated into a Discounted Cash Flow Rate of Return (DCFROR) analysis to characterize the economic performance of the system over a 30-year time horizon, considering important economic parameters and the time value of money. Results from the analysis are used to refine and optimize the system, define critical targets, and provide the pathway to desired economic outcomes.
Key Components of TEA:
Cost-Benefit Analysis: TEA involves a detailed examination of the costs associated with developing, deploying, and operating a technology. This includes capital costs, operational costs, and maintenance costs. On the benefit side, it assesses the economic gains, such as revenue generation and cost savings.
Financial Metrics: TEA employs financial metrics like net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and payback period to gauge the financial attractiveness of a technology. These metrics help determine whether the investment in the technology is economically sound over its lifecycle.
Risk Assessment: TEA considers uncertainties and risks associated with technological development and implementation. This involves analyzing factors that may impact costs and revenues, allowing stakeholders to make more informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
Sensitivity Analysis: TEA often includes sensitivity analysis to evaluate how changes in key parameters, such as input costs or market conditions, affect the economic feasibility of the technology. This helps in identifying critical variables and assessing their impact on project outcomes.
Life Cycle Costing: TEA takes a life cycle approach, considering costs and benefits over the entire lifespan of a technology. This includes manufacturing, operation, maintenance, and decommissioning costs. Evaluating the complete life cycle provides a more accurate representation of economic sustainability.
Policy Implications: TEA results can inform policy decisions by providing insights into the economic implications of adopting or supporting a specific technology. Policymakers can use this information to design effective incentives, subsidies, or regulations to promote economically sustainable technologies.
wHY PERFORM A TEA?
For startups navigating the complex landscape of emerging technologies, conducting Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) holds significant value in shaping their trajectory toward sustainable scaling. At the core of this methodology is a comprehensive evaluation that transcends mere technical feasibility, delving into the intricate interplay of economic factors. In the dynamic startup ecosystem, where resource allocation is a critical determinant of success, TEA serves as a strategic compass. By meticulously assessing the economic implications of technology development, startups can make informed decisions about investment, resource allocation, and overall feasibility, thereby mitigating risks associated with financial uncertainty.
One of the key advantages of TEA for startups lies in its ability to provide a holistic understanding of the costs and benefits associated with their technology. This insight is invaluable in establishing realistic financial projections, aiding startups in securing funding and attracting investors. Moreover, TEA's incorporation of financial metrics such as net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) facilitates the articulation of a compelling business case, bolstering a startup's credibility in the eyes of potential investors and stakeholders. By quantifying the economic viability of their technology, startups can strategically position themselves in the market, fostering trust and confidence among investors and partners.
TEA also equips startups with a robust risk assessment framework, a crucial asset in a landscape characterized by uncertainty and rapid change. Through sensitivity analysis, startups can identify potential vulnerabilities and devise contingency plans, enhancing their resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges. This proactive approach to risk management not only safeguards against potential pitfalls but also enhances a startup's adaptability and agility. Ultimately, TEA empowers startups to navigate the delicate balance between innovation and economic sustainability, providing a roadmap for scalable and resilient growth in the competitive landscape of emerging technologies.
